| Admissions | Aircraft | Aviation World | Ambassadors | Accreditation | A to Z Degree Fields | Books | Catalog | Colleges | Contact Us | Continents/States | Construction | Contracts | Distance Education | Emergency | Emergency Medicine | Examinations | English Editing Service | Economy and budget | Forms | Faculty | Governor | Grants | Hostels | Honorary Doctorate degree | Human Services | Human Resources | Internet | Investment | Instructors | Internship | Login | Lecture | Librarians | Languages | Manufacturing | Membership | Observers | Public Health | Publication | Professional Examinations | Programs | Professions | Progress Report | Recommendations | Ration food and supplies | Research Grants | Researchers | Students login | School | Search | Software | Seminar | Study Center/Centre | Sponsorship | Tutoring | Thesis | Universities | Work counseling |
| Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) | ||
| ||
| Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) | ||
| 1 | What have been various findings on or before October 27, 2021 in America? | Answer |
| 2 | Assessment of a patient by a physician. | Answer |
| 3 | What is an EMT? | Answer |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation | ||
| 6 |
What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation? How long will it last? Why is cardiopulmonary resuscitation important? What apparently happened? What should those who attended him on the spot have accomplished? How do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults who suddenly fall unconscious? When should you intubate a patient under emergency conditions? When should you start on-the-spot cardiopulmonary resuscitation? |
Answer |
| 7 | How do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults who suddenly fall unconscious? | Answer |
| 8 | When should you intubate a patient under emergency conditions? | Answer |
| 9 | When do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults? | Answer |
| 10 | What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation? | Answer |
| 11 | In what situations is a directive like "Do not Resuscitate" justified? | Answer |
| 12 | How many causes of a coma are there? | Answer |
| 13 | How many reversible causes of cardiopulmonary arrest are there? | Answer |
| 14 | Are there any differences between cardiac arrest and a coma? | Answer |
| 15 | Cardiac arrest: What are the symptoms? | Answer |
| 16 | What are the reversible causes of cardiac arrest? | Answer |
| 17 | What should happen on or after April 10, 2020, relevant to these issues? | Answer |
| 18 | When should the intervention relevant to such a patient happen? | Answer |
| 19 | What should be displayed on the Internet? | Answer |
Issues
Altered level of consciousness
|
Altered level of consciousness: What is it? Altered level of consciousness ranges from confusion to coma. 1. Confusion, 2. Delirium, 3. Lethargy and somnolence, 4. Obtundation, 5. Stupor, 6. Coma Some classify the range like this: 1. Confusion, 2. Disorientation, 3. Delirium, 4. Lethargy, 5. Stupor, 6. Coma. https://www.healthline.com explains it like this. 6 types of altered levels of consciousness: What are various examples?
How do you remember the causes of altered levels of consciousness? Remember at least 47 causes of coma. www.qureshiuniversity.com/coma.html Fix the underlying cause. A medical emergency physician has to do this. |
What is an EMT?
Emergency medical technician
What are the skills and knowledge required for this job?
|
Airway: Management
Airway management in unconscious non-trauma patient
Airway management in unconscious neck trauma patient
|
|
Airway management in unconscious non-trauma patient Airway management in unconscious neck trauma patient If the person is conscious, there is no need for further airway management. Conscious means able to hear, see, and talk normally. If the person is unconscious or there is an obstruction of the upper airway, airway management of the unconscious patient is required. How old is the patient? Compare the current respiratory rate of the patient with the age of the patient. Compare the current pulse rate of the patient with the age of the patient. What is the current respiratory rate of the patient? What is the current pulse rate of the patient? If there is no pulse and no respiratory rate for more than 10 seconds and the person was able to see, talk, and move their limbs a few minutes earlier, declare cardiopulmonary arrest and start cardiopulmonary resuscitation. What is the normal respiration rate for adults? 12 to 20 breaths per minute Pulse rate in adults: What is normal? 60 to 100 beats per minute. This is also known as the resting heart rate. Children What is the normal respiratory rate in children? Age Rate (in breaths per minute) Birth to 6 months 30 to 60 6 months to 1 year 30 to 50 1 to 3 years 24 to 40 3 to 5 years 22 to 34 5 to 12 years 16 to 30 12 to 18 years 12 to 20 The normal respiratory rate for children varies by age. Pulse rate in children: What is normal? Newborns 0 to 1 month old: 70 to 190 beats per minute Infants 1 to 11 months old: 80 to 160 beats per minute Children 1 to 2 years old: 80 to 130 beats per minute Children 3 to 4 years old: 80 to 120 beats per minute Children 5 to 6 years old: 75 to 115 beats per minute Children 7 to 9 years old: 70 to 110 beats per minute Children 10 years and older: 60 to 100 beats per minute If there is no pulse or no respiratory rate, the child was alive a few minutes before cardiopulmonary resuscitation is indicated. How do you administer cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a child? Take a look at this. Adult How do you know a human being has collapsed and needs cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Take a look at this. Is it normal? Yes, good. Look for other current problems. Is there a problem? Proceed relevant to the current problem in this situation. Where should you look for cyanosis in a white and black person? The best area to assess for cyanosis is where the outer layer of the skin is very thin, and the blood supply is very generous such as the cheeks, nose, ears, and oral mucosa. Is there cyanosis? If yes, how do you proceed? What needs to be done at this point relevant to the airway management of a patient? 1. Head-tilt-chin-lift technique (for nontraumatic medical conditions) 2. Jaw thrust technique (for neck injury) 3. Oropharyngeal airway (OPA) 4. Bag-valve-mask ventilation 5. Endotracheal intubation and ventilation (bag-valve-mask ventilation) 6. Endotracheal intubation and ventilation (bag-valve-mask ventilation or mechanical ventilator) 7. Administer oxygen via a nonrebreathing mask 8. Other 9. At this point do nothing relevant to airway management. Observe. Head-Tilt-Chin-Lift Technique: Basic Airway Maneuver (for nontraumatic medical condtions)  Jaw thrust technique: When is it required? Neck injury Jaw thrust technique: How do you do it? See the photograph. See the video Video Jaw thrust technique (for neck injury) 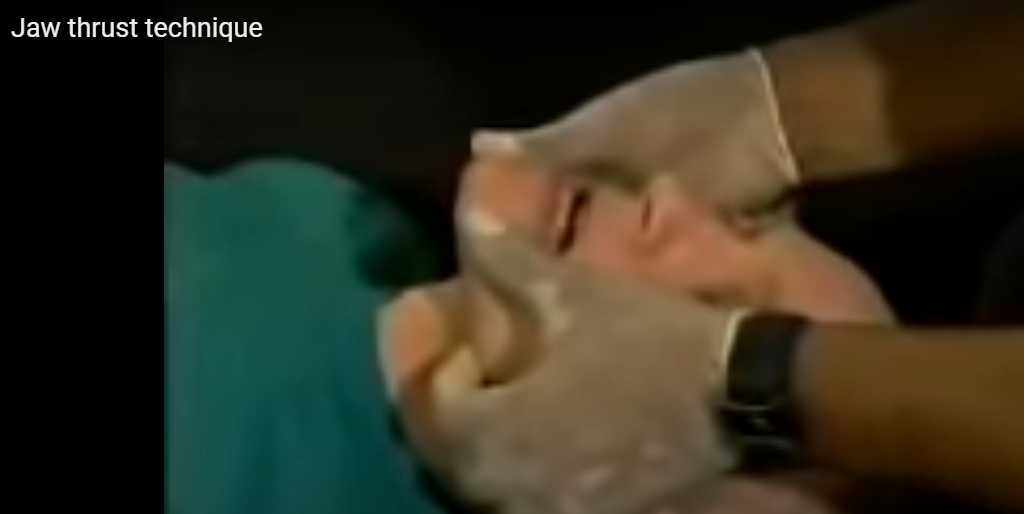 Video Oropharyngeal airway (OPA)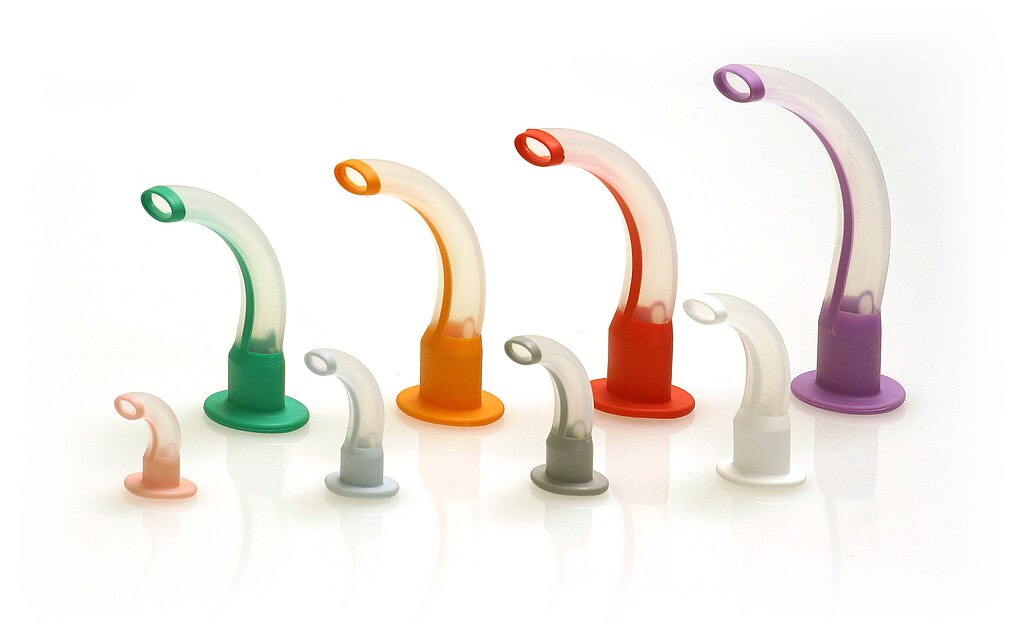 
How do you insert an oropharyngeal airway (OPA) of the correct size? The correct size of an oropharyngeal airway is chosen by measuring from the first incisors to the angle of the jaw. Or You should measure from the corner of the mouth to the earlobe. Which type of patients would most likely require the insertion of an oropharyngeal airway? A 40-year-old unconscious patient with slow, shallow respirations Signs of respiratory distress in children. (Tachypnea/Cyanosis) How do you insert an oropharyngeal airway? See the details How do you insert an oropharyngeal airway into the mouth of an infant? See the written details. See the photograph. See the video. Upon insertion of an oropharyngeal airway (OPA), the tip of the device should be positioned in what anatomical space? Laryngopharynx When is an oropharyngeal airway (OPA) used in this situation? As a convenient way to maintain an open airway in an unconscious patient. How To Do Bag-Valve-Mask (BVM) Ventilation Equipment for BVM Ventilation Gloves, mask, gown, and eye protection (ie, universal precautions) Oropharyngeal airways, nasopharyngeal airways, lubricating ointment Bag-valve apparatus PEEP valve Variably sized ventilation face masks Oxygen source (100% oxygen, 15 L/minute) Nasogastric tube Suctioning apparatus and Yankauer catheter; Magill forceps (if needed to remove easily accessible foreign bodies and patient has no gag reflex) to clear the pharynx as needed Pulse oximeter Capnography equipment Bag-valve apparatus 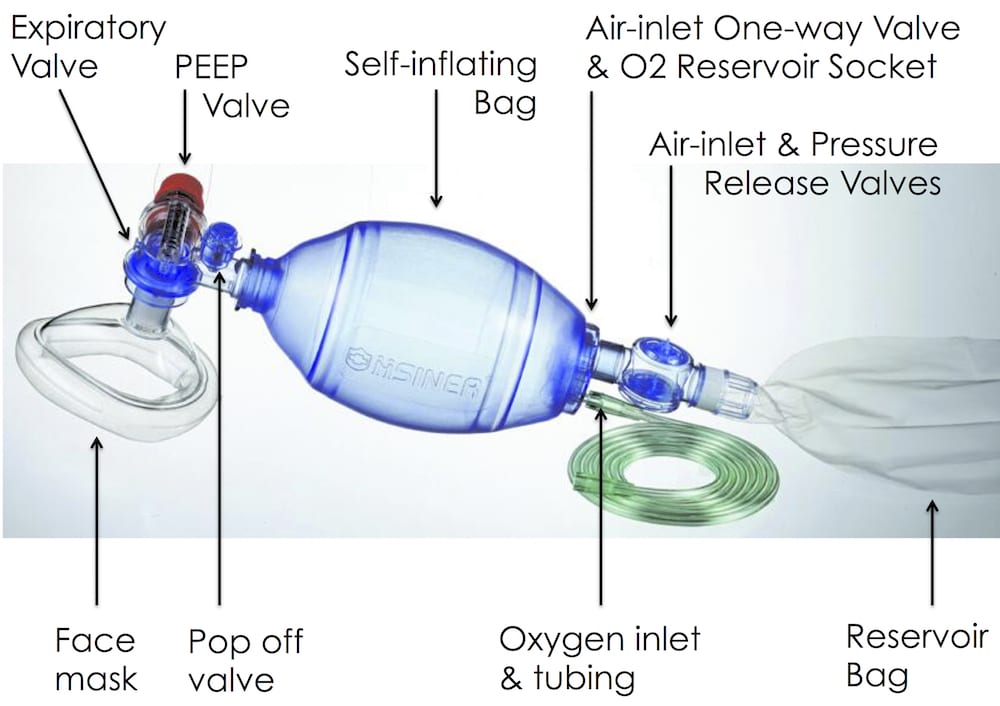
Additional Considerations for BVM Ventilation Two-person bag-valve-mask (BVM) ventilation is used whenever possible. Bag-valve-mask ventilation can be done with one person or two, but two-person BVM ventilation is easier and more effective because a tight seal must be achieved and this usually requires 2 hands on the mask. Unless contraindicated, a pharyngeal airway adjunct is used when performing BVM ventilation. An oropharyngeal airway is used unless the patient has an intact gag reflex; in such cases, a nasopharyngeal airway (nasal trumpet) is used. Bilateral nasopharyngeal airways and an oropharyngeal airway are used if necessary for ventilation. Characteristics that predict difficult bag ventilation (and can thus help troubleshoot if ventilation is difficult) are described by the mnemonic MOANS: M – Mask seal: Facial hair or facial trauma can interfere with creating an adequate seal. O – Obesity/Obstruction: Obesity can be a sign of increased soft tissue in the airway and thus may cause further occlusion when the patient is obtunded. Obstruction by other soft tissues or a foreign body can also prevent adequate ventilation. A – Age: Extremes of age can predict who may be difficult to ventilate using a BVM due to anatomical changes. N – No teeth. Performing BVM on a patient without teeth is usually ineffective; a supraglottic airway may be indicated. S – Snoring: Snoring respirations can indicate that soft tissue, usually the tongue, is occluding the airway and that repositioning (eg, head-tilt, chin-lift. jaw thrust) is required. A positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) valve may be used during BVM to improve oxygenation. PEEP can increase alveolar recruitment and thus oxygenation if oxygenation is compromised even with 100% oxygen due to atelectasis. PEEP has also been shown to prevent lung injury. However, PEEP should be used cautiously in patients who are hypotensive or pre-load dependent because it reduces venous return. When do you seal the mouth and nose during ventilation? What is CPAP? Continuous positive airway pressure What does the equipment for CPAP therapy look like? See the image. What are the medical uses of CPAP? 1. Adults with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea 2. Pre-term infants 3. Situations when the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli needs to be increased How does CPAP improve oxygenation and ventilation in patients with certain respiratory problems? It forces the alveoli open and increases the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli. When is nasal cannula most appropriately used in the prehospital setting? When the patient cannot tolerate a nonrebreathing mask. Prior to applying a nonrebreathing mask to a patient, what must you ensure? That the reservoir bag is fully inflated. What medical condition requires the administration of humidified oxygen? Croup What is apneic oxygenation? High-flow oxygen with a nasal cannula during the preoxygenation phase of endotracheal intubation When should an oxygen cylinder be taken out of service and refilled? When the pressure inside it is less than 500 psi At a flow rate of 6 L/min, a nasal cannula can deliver what approximate oxygen concentration? 44% Irregular respirations characterized by an increasing rate and depth of breathing followed by periods of apnea: What is it? Cheyne-Stokes respirations What is the difference among eupneic respirations, ataxic respirations, agonal respirations, and Cheyne-Stokes respirations? What is oxygen toxicity? Cellular tissue damage occurs from excessive oxygen levels in the blood. What are the structures of the lower airway: the trachea, bronchioles, epiglottis, and alveoli? The epiglottis is not part of the lower airway. Which of the following organs or tissues can survive the longest without oxygen: liver, muscle, heart, and kidneys? Muscle With a good mask-to-face seal and an oxygen flow rate of 15 L/min, the nonrebreathing mask is capable of delivering up to ______% inspired oxygen. 90 The pressure of gas in a full cylinder of oxygen is approximately _______ pounds per square inch (psi). 2,000 Which of the following structures is not among the upper airway: bronchus, larynx, oropharynx, and pharynx? Answer: Bronchus is not part of the upper airway. What is the most common cause of airway obstruction in an unconscious patient: the tongue, vomitus, blood clots, or aspirated fluid? Answer: The tongue Which of the following oxygen flowmeters is NOT affected by gravity and can be used in any position when attached to an oxygen cylinder: ball-and-float flowmeter, pressure-compensated flowmeter, vertical-position flowmeter, or Bourdon-gauge flowmeter? Bourdon-gauge flowmeter Which is a late sign of hypoxia? Cyanosis What is respiration? The process by which the body uses oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. Airway obstruction: What are the signs and symptoms? Agitation Alterations in normal breathing pattern, whether rapid or shallow breathing Choking or gagging Confusion Cyanosis (bluish-colored skin) Decreased breathing sounds in the lungs Difficulty breathing or no breathing Gasping for air High-pitched breathing noises called stridor or stertor, which may sound like wheezing Noisy breathing or wheezing Panic Struggling to breathe Sudden violent coughing Turning blue Unconsciousness Vomiting Cardio-respiratory arrest Emergency Medical Technician: Where do you start? Where do you end? Start with the guidelines displayed below. Most of the time you will find that an assessment by a medical emergency physician is required. What are the reasons? Here are the reasons. What is the diagnosis? What is the treatment? You will not be able to answer these questions. A medical emergency physician will be able to answer these questions. How do you do an assessment in a medical emergency situation? Start with the coma scale. This verifies the level of consciousness. Next check the pulse and respiratory rate. Check the blood pressure and temperature after this. What are various techniques required for the airway management of a patient? 1. Head-tilt-chin-lift technique (for nontraumatic medical conditions) 2. Jaw thrust technique (for neck injury) 3. Oropharyngeal airway (OPA) 4. Bag-valve-mask ventilation 5. Endotracheal intubation and ventilation (bag-valve-mask ventilation) 6. Endotracheal intubation and ventilation (bag-valve-mask ventilation or mechanical ventilator) 7. Other What is meant by BVM? Bag Valve Mask What is meant by minute volume? A patient may inhale 14 times per minute, taking in a full breath of 500 mL. 14bpm X 500 mL = 7000 mL per minute. What is a patent airway? An airway that is open and clear, and that will remain so, so that air may freely pass in and out of the lungs. What is inadequate breathing in this situation? Shallow breathing that is too slow or too fast, diminished breath sounds, abnormal noises, cyanosis, and/or inadequate minute volume. What is meant by artificial ventilation? The forcing of air or oxygen into lungs when a patient cannot breathe for themselves at all. What is hypoxia in this situation? Insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues of the body. What is meant by respiratory distress? An increase in breathing effort, accompanying a feeling of being short of breath. Oxygen cylinders are what color? Green A nasal canula is meant to deliver oxygen concentrations of: 24 – 44% Endotracheal intubation When do you do endotracheal intubation in a patient in a coma? If the coma scale is less than 8, do an endotracheal intubation in a coma patient. https://www.qureshiuniversity.com/endotrachealintubation.html |
Lifting and Moving Patients for EMTs
Lifting and Moving Patients
Assessment for Lifting and Moving Patients
|
|
Can the patient stand up? No: A stretcher is required. Yes: A wheelchair is required. What is required in this situation: a stretcher, wheelchair, or something else? Is the bed ready at the destination? What is the exact location at the destination? What is the approximate weight of the patient? If the patient weighs more than 250 pounds, four rescuers are required. How do you determine the approximate weight of the patient? Compare the patient to yourself and estimate an approximate weight. See if others have a record of weight of the patient. What are the five parts of assessment according to the National EMS education standard competencies? Scene size-up, primary assessment, history, secondary assessment, and reassessment During triage, what type of patient would receive a red triage tag? A patient who requires immediate treatment. What is the situation? 1. Moving a patient from the ground to a stretcher. 2. Loading a patient on a stretcher into the ambulance. 3. Moving a patient on a stretcher from the ambulance to a room or ward. 4. Moving a patient from a stretcher to a bed. 5. Helping a sitting patient from the bed to a wheelchair. 6. Helping a patient sit up in bed. 7. Using a turn sheet to move a patient up in bed. 8. Moving a patient from a bed to a stretcher. 9. Bringing a patient down the stairs. 10. Bringing a patient up the stairs on a stair chair. 11. Transferring a patient from a stretcher to a stair chair. Various videos have been displayed. If you have better video do email admin@qureshiuniversity.com. What is a building elevator? A building elevator (North American English) or lift (British English) is a machine that transports people or freight vertically between levels. Is there a building elevator? If yes, use the building elevator. What if there is no building elevator? Use a stair chair. When moving a conscious, weak patient down a flight of stairs, you should place a wheeled stretcher at the bottom of the stairs and carry the patient down the stairs using a stair chair. How do you operate a stretcher? See the types of stretchers. Carrying Devices Carrying devices relevant to lifting and moving patients: What are various examples? 1. Stretcher: a bed-like device for transporting patients.
B. Portable Stretcher: a light stretcher without wheels. C. Scoop Stretcher: a stretcher that can split apart to scoop up the patient on the ground from either side. D. Basket Stretcher: a stretcher with protective guards around the circumference (like a boat). E. Flexible Stretcher: a stretcher that is flexible and can fold. F. Bariatric Stretcher: a stretcher that can support up to 1600 pounds. For very large patients. 2. Stair Chair: a chair with handles to carry a sitting patient. 3. Backboard: a hard board used for spinal immobilization. Equipped with handholds and belts to fasten the patient. Can float in water. 4. Full Body Vacuum Mattress: a rigid mattress upon the application of a vacuum. Can provide a surface for spinal immobilization. 5. KED (Kendrick Extrication Device): a short backboard that provides full spinal immobilization. Can be applied when the patient is in a sitting position. 6. Wheelchair. 7. Sometimes a bed sheet or the equivalent may be required. Similar equipment is explained. Wheeled Stretcher
|
Patient assessment-related skills and knowledge.
|
Assessment of the patient in a medical emergency situation: Who must do the assessment? Medical emergency physician or the equivalent. If medical emergency technicians are given this responsibility, they will ultimately not be able to answer the relevant questions. What is the diagnosis? What is the treatment? These are the reasons a medical emergency physician has to be on site. An emergency medical technician (EMT) will get directions from the medical emergency physician. An emergency medical technician must focus on cardiopulmonary arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation, preferably under the supervision of a medical emergency physician. On or before October 25, 2021, existing EMT professionals were not able to do an assessment of the patient in the same way a specific physician does. In the end, you have to answer for this shortfall. An emergency medical technician must know everything about cardiopulmonary arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation, preferably under the supervision of a medical emergency physician or the equivalent. Other issues that a medical emergency physician or the equivalent must manage. Assessment of a patient by a physician. Here are further guidelines. |
Psychomotor tasks relevant to medical situations: What are various examples?
|
Patient assessment/management – Trauma Patient assessment/management – Medical (he or she cannot do) BVM ventilation of an apenic patient Oxygen administration by non-rebreather mask Cardiopulmonary arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation and AED skills and knowledge Bleeding control/shock management Upper airway adjuncts (oropharyngeal airway) and suction Mouth-to-mask ventilation Spinal immobilization (both seated and supine patient) Long bone fracture immobilization, joint dislocation immobilization, and traction splinting Bleeding control/shock management Upper airway adjuncts and suction Mouth-to-mouth ventilation with supplemental oxygen and supplemental oxygen administration to a breathing patient What was mentioned that is unreasonable? In addition, you must pass a psychomotor exam certified by your state. For information about the psychomotor exam, contact your EMT course instructor or state EMS office. Once you pass the exam, the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) will issue your certificate card. On or before October 24, 2021 they themselves did not know how to author research relevant to these issues in a question-and-answer format, as required, and display them publicly through the internet. What will they teach or assess in others that is fair and justified? If any entity claims to be a guide or authority, it must display the required questions and answers relevant to these issues that they have authored to resolve the problems. If they would have been competent on or before October 24, 2021, Dr. Asif Qureshi would not have authored these guidelines in a question-and-answer format to educate them at the executive level. They should be ashamed of themselves. They are taking income and keeping quiet. That is not fair or justified. Medications relevant to a medical emergency: What are various examples? Albuterol to treat asthma. Albuterol is a bronchodilator that relaxes muscles in the airways and increases air flow to the lungs. Albuterol inhalation is used to treat or prevent bronchospasm, or the narrowing of the airways in the lungs, in people with asthma or certain types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Epinephrine to treat anaphylactic shock. Narcan: Narcan is a medication to reverse the effects of an overdose. There are 2 types of short-acting beta agonists (SABAs): albuterol and levalbuterol. Short-acting anticholinergics Short-acting anticholinergics, such as Atrovent (ipratropium), are approved to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, your doctor may recommend using a short-acting anticholinergic with a SABA during an asthma attack to reduce the risk of being admitted to the hospital. Corticosteroids are medicines that reduce inflammation. These medicines include methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, prednisolone, and prednisone. Corticosteroids are sometimes prescribed to people having severe asthma attacks and can be taken by mouth, through an injection, or intravenously (through an IV). This treatment often lasts 5 to 7 days. Long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) Intravenous fluids skills and knowledge http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/intravenousfluids.html Specific physicians Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html |
Quiz issues.
Additionally, inserted in the previously listed topic areas will be questions requiring knowledge of pharmacology, patient assessment, and pediatrics. You should also take the time to review these areas of study as you prepare for our practice tests and the official testing session.
You will be assessed on psychomotor tasks throughout your EMT coursework. During this time, you will need to prove that you can perform these tasks: patient assessment/management of a trauma patient, patient assessment/management of a medical patient, cardiac arrest management/AED, bag-valve-mask ventilation of an apneic patient, spinal immobilization (both seated and supine patient), long bone fracture immobilization, joint dislocation immobilization, traction splinting, bleeding control/shock management, upper airway adjuncts and suction, mouth-to-mouth ventilation with supplemental oxygen, and supplemental oxygen administration to a breathing patient.
Additionally, you must pass a psychomotor exam certified by your state. For information about the psychomotor exam, contact your EMT course instructor or state EMS office.
Once you pass the exam, the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) will issue your certificate card, which can be downloaded from their website. If you do not pass the test, you will be sent a detailed analysis of your strengths and weaknesses. This will enable you to study further in areas of difficulty, as assessed by the exam. When you retake the exam, you will not see any of the items you missed the first time. They will be “masked†by the computer.
If you did not pass the cognitive exam, you can apply to retest 15 days after the last exam and have six chances to pass. You may take the NREMT test up to three times without further training. After that, you must provide documentation of remedial training to retake up to three more times. Following the sixth unsuccessful attempt, you will be required to retake the entire EMT training course before retesting.
|
Job Duties What are the duties and responsibilities of this job? What does an EMT do? EMTs and paramedics typically do the following: •Respond to 911 calls for emergency medical assistance, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or bandaging a wound •Assess a patient’s condition and determine a course of treatment •Create a patient care report; documenting the medical care they gave the patient •Follow guidelines that they learned in training and that they receive from physicians who oversee their work •Help transfer patients to the emergency department of a healthcare facility and report their observations and treatment to the staff •Use backboards and restraints to keep patients still and safe in an ambulance for transport •Replace used supplies and check or clean equipment after use Career Overview Emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics care for the sick or injured in emergency medical settings. People’s lives often depend on their quick reaction and competent care. EMTs and paramedics respond to emergency calls, performing medical services and transporting patients to medical facilities. A 911 operator sends EMTs and paramedics to the scene of an emergency, where they often work with police and firefighters. Duties EMTs and paramedics typically do the following: •Respond to 911 calls for emergency medical assistance, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or bandaging a wound •Assess a patient’s condition and determine a course of treatment •Follow guidelines learned in training or received from physicians who oversee their work •Use backboards and restraints to keep patients still and safe in an ambulance during transport •Help transfer patients to the emergency department of a healthcare facility and report their observations and treatment to the staff •Create a patient care report, documenting the medical care given to the patient •Replace used supplies and check or clean equipment after use When taking a patient to a hospital, one EMT or paramedic may drive the ambulance while another monitors the patient's vital signs and gives additional care. Some paramedics work as part of a helicopter's flight crew to transport critically ill or injured patients to a hospital. EMTs and paramedics also transport patients from one medical facility to another. Some patients may need to be transferred to a hospital that specializes in treating their injury or illness or to a facility that provides long-term care, such as a nursing home. If a patient has a contagious disease, EMTs and paramedics decontaminate the interior of the ambulance and may need to report the case to the proper authorities. The specific responsibilities of EMTs and paramedics depend on whether they are an EMT or EMT-Basic, Advanced EMT, or paramedic; and the state they work in. An EMT, also known as an EMT-Basic, cares for patients at the scene of an incident and while taking patients by ambulance to a hospital. An EMT-Basic has the skills to assess a patient's condition and to manage respiratory, cardiac, and trauma emergencies. An Advanced EMT, also known as an EMT-Intermediate, has completed the requirements for the EMT level, as well as instruction in more advanced medical procedures, such as administering intravenous fluids and some medications. Paramedics provide more extensive prehospital care than do EMTs. In addition to being able to carry out the tasks of EMTs, paramedics can give medications orally and intravenously, interpret electrocardiograms (EKGs)â€â€used to monitor heart functionâ€â€and use other monitors and complex equipment. The specific tasks or procedures EMTs and paramedics are allowed to perform at any level vary by state. Work Environment Emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics held about 239,100 jobs in 2012. They work both indoors and outdoors, in all types of weather. Their work is physically strenuous and can be stressful, sometimes involving life-or-death situations and patients who are suffering. Most paid EMTs and paramedics work in metropolitan areas. Volunteer EMTs and paramedics are more common in small cities, towns, and rural areas. These individuals volunteer for fire departments, providers of emergency medical services, or hospitals and may respond to only a few calls per month. Injuries and Illnesses EMTs and paramedics have a higher rate of injuries and illnesses than the national average. They are required to do considerable kneeling, bending, and lifting while caring for and moving patients. They may be exposed to contagious diseases, such as hepatitis B and AIDS. Sometimes they can be injured by mentally unstable or combative patients. These risks can be reduced by following proper safety procedures, such as waiting for police to clear an area in violent situations or wearing gloves while working with a patient. Work Schedules Most paid EMTs and paramedics work full time. About 1 in 3 worked more than 40 hours per week in 2012. Because EMTs and paramedics must be available to work in emergencies, they may work overnight and on weekends. Some EMTs and paramedics work shifts in 12- or 24-hour increments. Volunteer EMTs and paramedics have variable work schedules. Education and Training Emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics must complete a postsecondary educational program. All states require EMTs and paramedics to be licensed; requirements vary by state. Education Both a high school diploma or equivalent and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) certification are prerequisites for most postsecondary educational programs in emergency medical technology. Most of these programs are postsecondary non-degree award programs that can be completed in less than 1 year; others last up to 2 years. Paramedics, however, may need an associate’s degree. Educational programs in emergency medical technology are offered by technical institutes, community colleges, and facilities that specialize in emergency care training. High school students interested in becoming EMTs or paramedics should take courses in anatomy and physiology. Programs at the EMT level include instruction in assessing patients' conditions, dealing with trauma and cardiac emergencies, clearing obstructed airways, using field equipment, and handling emergencies. Formal courses include about 150 hours of specialized instruction, and some instruction may take place in a hospital or ambulance setting. Programs at the Advanced EMT level typically requires about 300 hours of instruction based on the scope of practice. At this level, people must complete the requirements for the EMT level as well as more advanced ones, such as using complex airway devices, intravenous fluids, and some medications. Paramedics have the most advanced level of education. They must complete EMT and Advanced EMT levels of instruction, along with courses in advanced medical skills. Community colleges and technical schools may offer these programs, which require about 1,200 hours of instruction and may lead to an associate's degree. Paramedics’ broader scope of practice may include stitching wounds or administering intravenous medications. Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) certifies EMTs and paramedics. All levels of NREMT certification require completing a certified education program and passing the national exam. The national exam has both written and practical parts. All states require EMTs and paramedics to be licensed; requirements vary by state. In most states, an individual who has NREMT certification qualifies for licensure. In others, passing an equivalent state exam is required. Usually an applicant must be over the age of 18. Many states require background checks and may not give a license to an applicant who has a criminal history. Although some emergency medical services hire separate drivers, most EMTs and paramedics take a course requiring about 8 hours of instruction before they can drive an ambulance. Important Qualities Compassion. EMTs and paramedics must be able to provide emotional support to patients in an emergency, especially patients who are in life-threatening situations or extreme mental distress. Interpersonal skills. EMTs and paramedics usually work on teams and must be able to coordinate their activities closely with others in stressful situations. Listening skills. EMTs and paramedics need to listen to patients to determine the extent of their injuries or illnesses. Physical strength. EMTs and paramedics need to be physically fit. Their job requires a lot of bending, lifting, and kneeling. Problem-solving skills. EMTs and paramedics need strong problem-solving skills. They must be able to evaluate patients’ symptoms and administer the appropriate treatments. Speaking skills. EMTs and paramedics need to be able explain procedures to patients, give orders, and relay information to others. Pay The median annual wage for emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics was $31,020 in May 2012. The median wage is the wage at which half the workers in an occupation earned more than that amount and half earned less. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $20,180, and the top 10 percent earned more than $53,550. Most paid EMTs and paramedics work full time. About 1 in 3 worked more than 40 hours per week in 2012. Because EMTs and paramedics must be available to work in emergencies, they may work overnight and on weekends. Some EMTs and paramedics work shifts in 12- or 24-hour increments. Volunteer EMTs and paramedics have variable work schedules. |
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
|
What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique useful when someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped. How long will it last? This is usually done for 15 to 30 minutes. Why is cardiopulmonary resuscitation important? These examples will help you understand. Case #1 What apparently happened?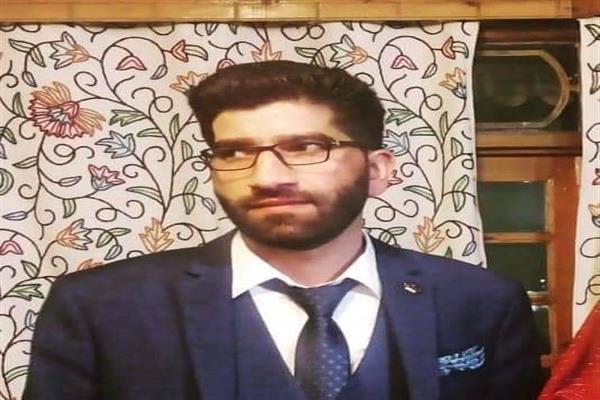 
Date: Thursday, October 1, 2020 Name: Javid Ahmad Age: 31 Incident: Suddenly fell unconscious. He was travelling in a passenger bus. Location of incident: Pattan area in Kashmir. He was on his way to Srinagar from the Watergam area of the Baramulla district. Javid was a resident of the Watergam area of Rafiabad. He was rushed to a nearby hospital, where doctors declared him dead. He was a senior correspondent of a Srinagar-based English daily. He died on October 1, 2020. The causes and circumstances of his death mentioned heart attack. This needs further investigation. A young man rarely has a heart attack (myocardial infarction). Cardiac arrest is the last scenario in all human deaths. There can be other causes and circumstances. Questions that need further answers from specific physicians: What were the causes and circumstances of his death? How did you verify the causes and circumstances of his death? What should those who attended him on the spot have accomplished? Those who saw him suddenly fall unconscious should have started cardiopulmonary resuscitation on the spot. How do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults who suddenly fall unconscious? Start by asking, “How are you?†You can translate this into the local language. If there is no reply, tap or shake the person’s shoulder and loudly ask, “Are you okay?†If there is no reply, place the person on the ground. Check to see if the person can hear, see, and talk. Verify if there is a pulse and breathing. If there is no pulse and no breathing for 10 seconds, begin chest compressions. Give 30 chest compressions before giving two rescue breaths. Call for emergency or more help. Give them the location. When should you intubate a patient under emergency conditions? When the pulse oximetry (O2 saturation) is less than 90%, without any underlying respiratory conditions or hypoxemia. Severe hypoxemia occurs when the O2 saturation falls below 85%. If there is a history of suddenly falling unconscious, intubate the patient. Place the patient on a mechanical ventilator. See further guidelines. Who officially received remuneration, income, and grants to circulate these guidelines on or before October 1, 2020? Stop their income, remuneration, and grants. Suspend them from services. Terminate the services of those who were alerted ahead of time. Record the findings in their service book on or before October 1, 2020. Failure to provide public health guidelines publicly at least through internet that they have responsibilities. Circuit Court supervision of all grants resources, income, salary, human resources for these services including for www.grants.gov. They are taking salaries, grants, resources and keeping quite without public services that is not justified. Here are further guidelines. When should you start on-the-spot cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Was the patient alive a few minutes before? Is there a few minutes history of injury? Is there no pulse, breath movement, or heart sounds? Are there no signs of rigor mortis? Are extremities of victim warm like a living human being? If yes, start cardiopulmonary resuscitation. How do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults who suddenly fall unconscious? Start by asking, “How are you?†You can translate this into the local language. If there is no reply, tap or shake the person’s shoulder and loudly ask, “Are you okay?†If there is no reply, place the person on the ground. Check to see if the person can hear, see, and talk. Verify if there is a pulse and breathing. If there is no pulse and no breathing for 10 seconds, begin chest compressions. Give 30 chest compressions before giving two rescue breaths. Call for emergency or more help. Give them the location. When should you intubate a patient under emergency conditions? When the pulse oximetry (O2 saturation) is less than 90%, without any underlying respiratory conditions or hypoxemia. Severe hypoxemia occurs when the O2 saturation falls below 85%. If there is a history of suddenly falling unconscious, intubate the patient. Place the patient on a mechanical ventilator. See further guidelines. When do you start cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults? CPR is required someone's breathing or heartbeat has stopped, as in cases of electric shock, drowning, or heart attack. CPR is a lifesaving procedure in this situation. What is cardiopulmonary resuscitation? Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a combination of rescue breathing and chest compressions. Rescue breathing provides oxygen to a person's lungs. Chest compressions keep the person's blood circulating. Permanent brain damage or death can occur within minutes if a person's blood flow stops. Therefore, you must continue these procedures until the person's heartbeat and breathing return, or trained medical help arrives. In what situations is a directive like "Do not Resuscitate" justified? Old age more than 95 years with known complications. How many causes of a coma are there? At least 47. You have to correlate the causes of a coma and the causes of reversible cardiopulmonary arrest. How many reversible causes of cardiopulmonary arrest are there? At least 14. The treatment is to fix the underlying cause. Are there any differences between cardiac arrest and a coma? Yes. Cardiac arrest: What are the symptoms? Sudden collapse No pulse No breathing Loss of consciousness Sometimes other signs and symptoms occur before sudden cardiac arrest. These might include: Chest discomfort Shortness of breath Weakness Palpitations In a coma, the individual has a pulse and is breathing. In a coma, the individual cannot engage in spontaneous eye opening, talking, or walking. What are the reversible causes of cardiac arrest? Hypoxia Hypovolemia Hypoglycemia Hypokalemia Hypothermia Hydrogen ion excess (acidosis) Hyperkalemia Tamponadeâ€â€cardiac Tension pneumothorax Toxins Thrombosis (pulmonary embolus) Thrombosis (myocardial infarction) Trauma Tachycardia ventricular. Pulseless cardiac arrest, including PEA, asystole, ventricular fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia. The treatment for pulseless ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia is defibrillation. What should happen on or after April 10, 2020, relevant to these issues? I/we should not wait until a patient dies and then ask the medical examiners office to determine the causes/circumstances of death. Intervention should happen before the death of the patient. When should the intervention relevant to such a patient happen? As soon as the patient goes into coma and before death. All governors and state department of public health directors must alert all medical emergency and critical care units about these facts. As soon as a patient goes into a coma, the state should display the patient’s profile and facts on the Internet. The state department of public health should display a list of coma patients. On or after April 11, 2020, make this an emergency public health law. When a patient goes into a coma, his/her profile with answers to these questions must be displayed on the Internet. For example: Illinois coma patient list with date and time of circulation. New York coma patient list with date and time of circulation. California coma patient list with date and time of circulation. Spain coma patient list. Italy coma patient list. Wuhan coma patient list Kashmir coma patient list. Similar entities. Patients are dying from causes and circumstances other than the coronavirus. Doctor Asif Qureshi will provide further emergency medicine doctor guidelines and critical care doctor guidelines on the Internet. The facts must be updated 24/7 on the Internet. If video conferencing is possible, it should be displayed. What should be displayed on the Internet? Questions you need to answer on the Internet. What was the date and time circumstances when the patient went into a coma? What is the name of the patient? What is the date of birth of the patient? What is the name of the treating doctor seeing the patient every day, face to face and in person? What is the name(s) of the nurse(s) who see the patient every day? At what location is this patient receiving treatment? What is the patient’s medical history of the main medical problem, from first emergence until now? What other medical issues does the patient have? What are the patient’s vitals, including date, time, and location? What are the last known and previous pulse oximetry blood oxygen saturation results? What are the last known and previous blood biochemistry results of the patient? What is the diagnosis? What is the treatment? What should be included in a review of the diagnosis? What should be included in a review of the treatment? |
Medical Emergencies
|
What types of physicians must be on an ambulance? If a physician medical emergency responder must respond to on spot medical emergency through emergency medical services with an ambulance, why do we need EMR (Emergency Medical Responder), EMT (Emergency Medical Technician), AEMT (Advanced Emergency Medical Technician), Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Instructor, Paramedic as medical emergency responders? What do states have to do about emergency medical responders? Are there other jobs like this? How long does it take to be a paramedic? What's the Difference Between an EMT and a Paramedic? What is the difference between an EMT and EMS? How do EMTs interact with other health professions workers? What was it like to work as an EMT? How do you become an EMT? Is this a paid or volunteer position? What is the time commitment? What advice do you have for someone interested in becoming an EMT? What is the difference between an EMT and an EMR? What is an emergency medical responder? |
Medical Emergencies  What types of physicians must be on an ambulance? This ambulance must have a physician medical emergency responder (first responder). The physician medical emergency responder (first responder) is also known as emergency medicine specialist (first responder). If a physician medical emergency responder must respond to on spot medical emergency through emergency medical services with an ambulance, why do we need EMR (Emergency Medical Responder), EMT (Emergency Medical Technician), AEMT (Advanced Emergency Medical Technician), Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Instructor, Paramedic as medical emergency responders? There are few physician medical emergency responders, physician medical emergency rooms and physician intensive care units available. Because of the lack of physician medical emergency responders, EMRs (Emergency Medical Responder), EMTs (Emergency Medical Technician), AEMTs (Advanced Emergency Medical Technician), and Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Instructors, paramedics are required in certain situations. What do states have to do about emergency medical responders? Standardize emergency medical responder levels. Emergency medical specialists (first responders) also known physician medical emergency responders or the equivalent must be first responders among emergency medical responders. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/medicalemergency.html Are there other jobs like this? EMR (Emergency Medical Responder) EMT (Emergency Medical Technician) AEMT (Advanced Emergency Medical Technician) Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Instructor Emergency Medical Services Lab Assistant Paramedic How long does it take to be a paramedic? Steps to Becoming a Paramedic/EMT. EMT basic training (EMT-B) takes anywhere from six months to two years to complete, depending on the institution. These programs are offered at technical institutes and community colleges and typically include 120 to 150 hours of coursework. What's the Difference Between an EMT and a Paramedic? EMT's and Paramedics are well trained healthcare professionals whom respond to medical and traumatic emergencies in the pre-hospital setting. The primary difference between a Paramedic and an EMT is the amount of education and their scope of practice (what they are allowed to do). EMTs usually complete a course such as ______'s EMT course that is about 120-150 hours in length. Paramedic courses can be between 1,200 to 1,800 hours. EMT and paramedic courses consist of lectures, hands-on skills training, and clinical and/or field internships. EMTs are educated in many skills including CPR, giving patients oxygen, administering glucose for diabetics, and helping others with treatments for asthma attacks or allergic reactions. With very few exceptions, such as in the case of auto-injectors for allergic reactions, EMTs are not allowed to provide treatments that requiring breaking the skin: that means no needles. Paramedics are advanced providers of emergency medical care and are highly educated in topics such as anatomy and physiology, cardiology, medications, and medical procedures. They build on their EMT education and learn more skills such as administering medications, starting intravenous lines, providing advanced airway management for patients, and learning to resuscitate and support patients with significant problems such as heart attacks and traumas. What is the difference between an EMT and EMS? Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) are the most common type of providers in all of EMS. They are the entry-level patient care provider followed by EMT-Intermediates (in some states) and then paramedics. EMTs are sometimes referred to as EMT-Basics or EMT-1s. However, do not be fooled by the term "entry-level." What is the difference between an EMT and an EMR? The biggest differences between paramedics, EMR's and EMTs are the training and the scope of practice (what they are allowed to do).EMR's usually receive 80 – 100 hours of training, Basic EMTs usually receive 120 – 180 hours of training, while paramedics get anywhere from 1,200 hours to 1,800 hours of training. What is an emergency medical responder? Emergency medical responders can range from bystanders with Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) certification to trained professional rescuers such as First Responders, EMT-Basics/Intermediates, Paramedics, Nurses, or Doctors. Emergency medical responders are people who are specially trained to provide out-of-hospital care in medical emergencies. There are many different types of emergency medical responders, each with different levels of training, ranging from first aid and basic life support. Critical Care Paramedics This course is designed to prepare paramedics to provide advanced critical care during inter-facility transports, including performing advanced clinical patient assessments and providing invasive care beyond the standard scope of advanced pre-hospital care. Includes modes of transport, flight physiology, barophysiology and transfer considerations, including safety, patient packaging and practice in a closely confined space, airway and ventilation management including surgical airways and ventilators, CPAP and BiPAP, thoracostomy, and chest drainage maintenance, central venous lines, expanded pharmacologic formulary, interpretation of laboratory data, 12-lead ECG interpretation, monitoring and maintaining and IABP, and hemodynamic monitoring. Instruction is provided in both didactic and clinical settings. |
Traumatic injury
|
The Revised Trauma Score (RTS) What is the Revised Trauma Score? The Revised Trauma Score is made up of three categories: the Glasgow Coma Scale, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate. The score ranges from 0 to 12. In START triage, a patient with an RTS score of 12 is labeled delayed, 11 is urgent, and 3–10 is immediate. Those who have an RTS below 3 are declared dead or highly unlikely to survive. What does a lower Revised Trauma Score indicate? A lower score indicates a higher severity of injury. How do you calculate the Revised Trauma Score?  Here are further guidelines. |
What problems, complaints, incidents, and issues need on-the-spot diagnosis and treatment?
| 1. Burns |
|
2. Cardiopulmonary arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation Make sure you know everything about comas and reversible causes of cardiac arrest. |
| 3. Drowning |
| 4. Feelings of committing suicide or murder. A person has a feeling of harming others or you: How will you manage the situation? The person feels you have intentionally inflicted harms and then maintained criminal silence. |
| 5. Human pregnancy emergencies, maliciously impregnated (medico-legal case that needs emergency contraception), and spontaneous vaginal delivery |
| 6. Seizures |
| 7. Sudden unconsciousness at home. |
| 8. Survival needs |
| 9. Swallowing a poisonous substance |
| 10. Trauma |
| 11. Unconsciousness at a public location |
|
Specific physicians Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html |
|
Who received these facts? Brendan McCrudden, Commander 5400 North Lincoln Avenue Chicago, IL 60625 Email: CAPS020District@chicagopolice.org Phone: 312-742-8714, 312-742-8715 Fax: 312-742-8803 https://home.chicagopolice.org/about/police-districts/20th-district-lincoln/ When did they receive these facts? Last Updated: February 18, 2024 What did they receive? |
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
How do you know a human being has collapsed and needs cardiopulmonary resuscitation?
Start with the coma scale.
|
The International Red Cross did not display these 10 questions on or before August 17, 2023. Other executive healthcare resources did not display these 10 questions on or before August 17, 2023. Dr. Asif Qureshi training patrolling police officers to carry out cardiopulmonary resuscitation: What do you have to do? Cardiopulmonary resuscitation for adults. 1. Assessment Here are further guidelines. Have you answered 10 questions relevant to this situation? 1. Where is the patient now? 2. Is the person on the ground? 3. Ask: How are you? No reply. 4. Are you okay? No reply. 5. Was the patient able to see, talk, and move a few minutes earlier? Yes. 6. Can the patient open both eyes spontaneously? No. 7. Can the patient talk or make noises relevant to age? No. 8. Can the patient walk or move their extremities relevant to age? No. 9. Put your hand on the radial pulse. Is there a pulse? No. 10. Put your hand on the chest. Is there respiratory movement? No. The patient was able to see, talk, and move a few minutes earlier. The patient cannot open both eyes spontaneously, talk or make noise relevant to age, and/or walk or move extremities relevant to age. There is no pulse, no breath movement, and/or no heart sounds at this point. Start cardiopulmonary resuscitation. These guidelines are for a person or victim who is more than 18 years old. If there is no pulse and no breathing for 10 seconds, begin chest compressions. Give 30 chest compressions before giving two rescue breaths. Hands-only cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Traditional cardiopulmonary resuscitation with breaths. See the 9 steps of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. |
Crisis
|
What is a crisis? How do you manage crisis? What should a state display publicly? Who is on duty to manage a crisis? What is the contact information? Have they established an Internet resource? What are examples of crises? What are examples of mishandled crises? Do those on duty know what a crisis is? Can those on duty manage a crisis? How do you manage a crisis? How should you manage a crisis? What is an example of a smoldering crisis? www.nazianazirqazi.org. This is an example of a smoldering crisis. |
Last Updated: February 16, 2024